Table of Contents
After years working with SEO agencies and clients, we’ve noticed that most successful SEO practitioners are very serious about how they track their SEO results.
That makes sense: when you know what aspects of your SEO strategy perform well and what not, you can scale up successful strategies and quickly cut off wasteful.
In this article, we’ll walk you through our process of tracking SEO performance with precision and priority in mind.
1. What to Track: Primary Success Metrics
Spending time on tracking irrelevant or vanity metrics is one of the primary reasons behind the lack of success in SEO. Common examples of metrics that hinder your growth are keyword rankings for keywords that don’t bring any traffic, number of blog posts published, or traffic that doesn’t convert.
To avoid that, always prioritize SEO metrics that can be directly related to your business bottom line.
Below are the most productive SEO metrics to track:
- Conversions. SEO results can be tied directly to conversion goals such as form submissions, accounts registrations, email signups, and so on. Although it might require additional effort to set up proper conversion tracking, it’s well worth the time spent.

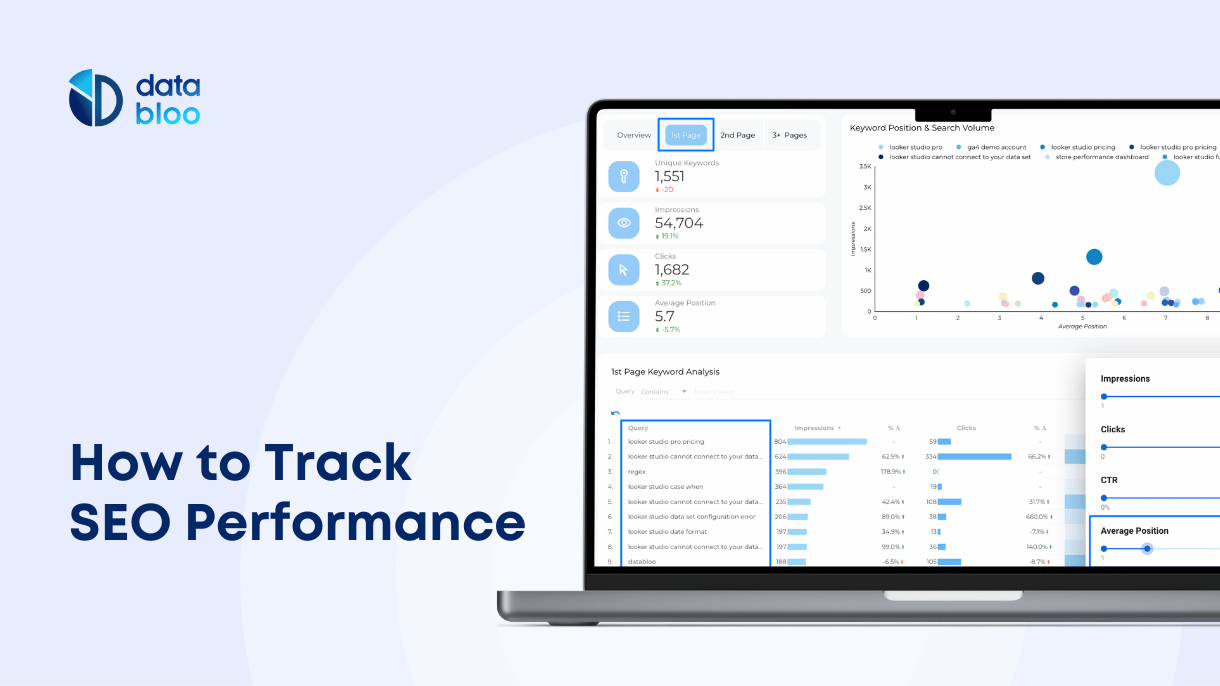
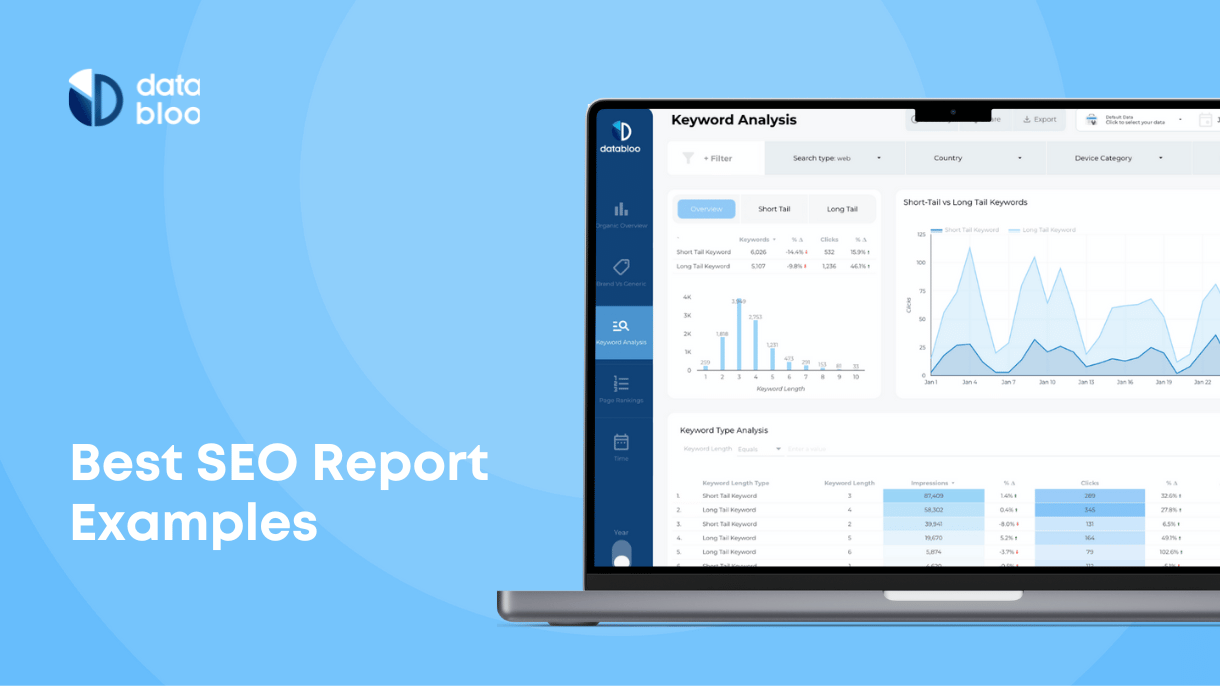
- Keyword rankings. Not all keywords, even when you rank high for them, will generate equal results, and with regular SERP fluctuations you will quickly get confused when tracking dozens of different keywords. Avoid tracking many keywords (ecommerce SEO is an exception) and focus on a small number of ultra important keywords that you want to rank for.

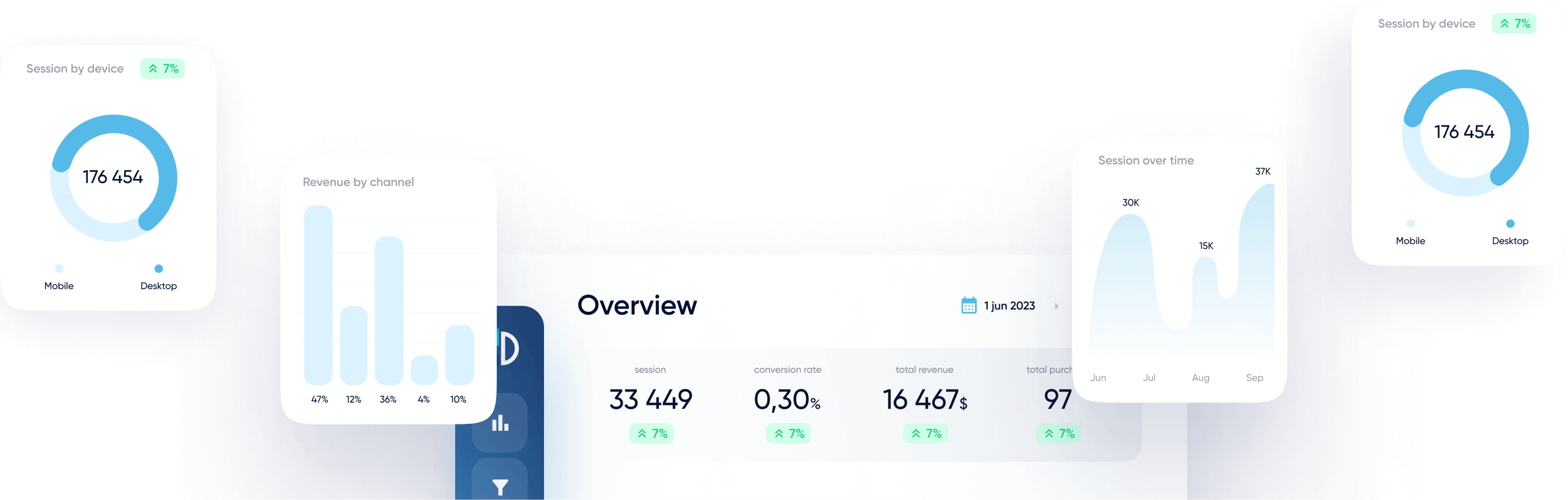
- Organic traffic. Organic traffic is one of the most common metrics to track in SEO, and one of the most important. Tracking traffic is useful for overall indication of SEO results or for spotting bad effects such as Google penalization or increasing SERP competition. Plenty of sub-metrics of traffic such as country of origin, traffic sources, first page visited, and traffic by device are extremely useful to better understand your audience and impact of specific SEO campaigns.

- Website performance metrics. Page loading times and overall website speed directly correlate to search performance in many ways, so make sure to track these metrics for your most important pages at least monthly to keep them stable or to improve consistently.
2. What Else To Track: (Secondary Contextual Metrics)
While primary metrics provide a broad overview of your SEO performance, secondary metrics offer deeper insights into specific aspects of your SEO strategy. It’s best to create separate reports for each context to maintain clarity and focus.
Local SEO
Key metrics for tracking the efficiency of local SEO campaigns:
- Google Business Profile (GBP) Insights. These metrics directly reflect your local visibility and user engagement. They show how often your business appears in local searches and maps, and how users find your listing: keywords and volume of searches, website interactions, and photo views. You can easily pull this insights using our free Google Business Profile Connector for Looker Studio.
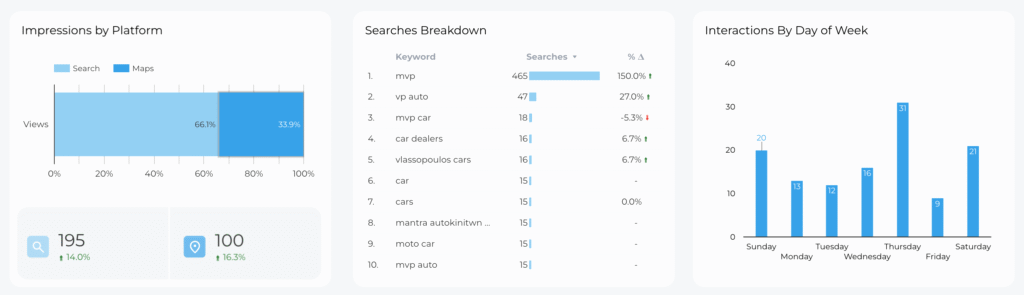
- Local pack rankings. Position in the local 3-pack for target keywords and frequency of appearance in local pack results. The local pack is prime real estate in search results. Higher and more frequent appearances directly correlate with increased visibility and potential foot traffic. Track these rankings for different geo-locations relevant to your business, not just your immediate area. This helps you understand your reach and identify expansion opportunities.
- Citations. Consistent citations build trust with search engines and users. They’re a fundamental ranking factor for local SEO. Use a citation tracking tool to monitor consistency. Focus on quality over quantity – aim for citations from authoritative, relevant local directories.
- Local keyword Rankings. Rankings for “near me” and “[service] in [location]” queries. And rankings for local long-tail keywords. These rankings show how well you’re capturing local search intent and competing for location-specific queries.
Ecommerce SEO
Key metrics for tracking the efficiency of ecommerce SEO campaigns:
- Organic product visibility. Rankings for product and category pages. Higher rankings lead to increased organic traffic and potential sales. Track both broad and long-tail product keywords.
- Organic revenue and transactions. Shows direct impact of SEO on the bottom line. Helps identify which products and categories perform well in organic search.
- Average order value (AOV) from organic traffic. Indicates quality of organic traffic. Higher AOV suggests SEO is attracting high-intent customers.
- Conversion rate from organic search. Shows how effectively organic visitors become customers. Low rates may indicate issues with relevance or user experience.
- Shopping feed performance. Monitor impressions, clicks, and CTR in Google Shopping. Helps optimize product feed and compare with competitors.
Track bi-weekly or more frequently. Consider context like seasonality and promotions when analyzing trends.

PR and Link Building Campaigns
Key SEO metrics for tracking the efficiency of PR and link building efforts:
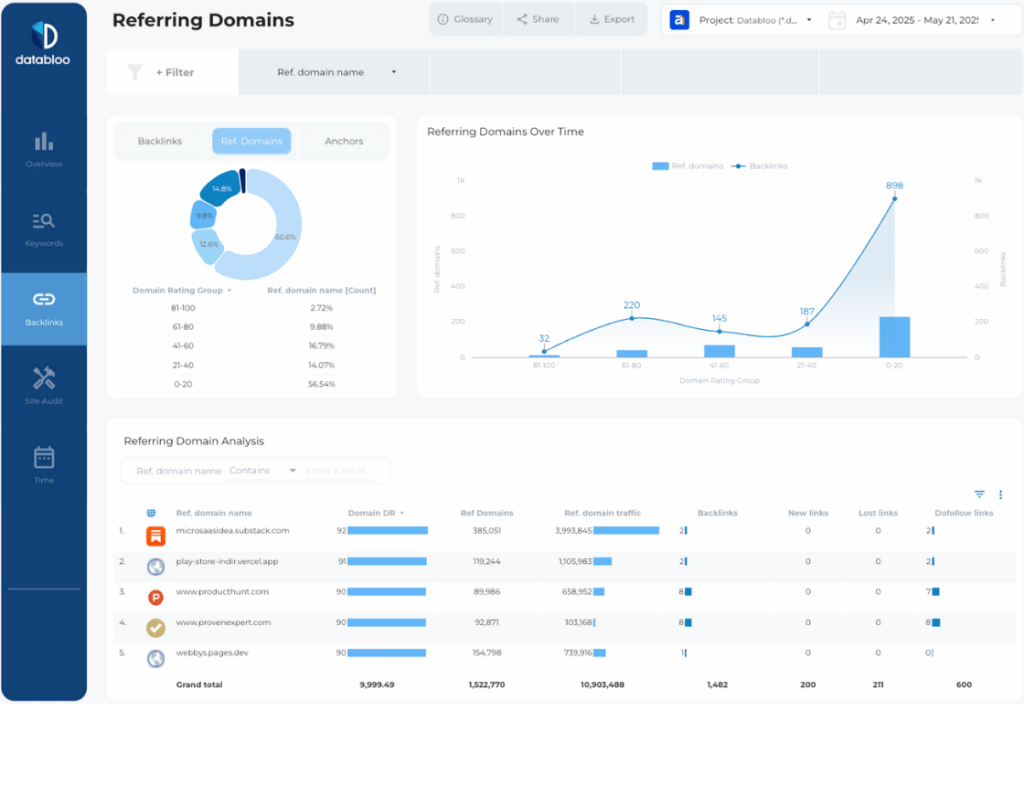
- New backlinks acquired. Tracks the quantity of new links over time. Indicates campaign success in generating link opportunities. Monitor both the total number and rate of acquisition.
- Backlink quality. Assess links based on domain authority, relevance, and traffic potential. Quality often matters more than quantity. Focus on gaining links from authoritative, topically relevant sites.
- Referring domains. Count of unique domains linking to your site. Diverse link profiles from multiple domains typically carry more SEO value than multiple links from fewer sites.
- Anchor text distribution. Analyze the text used in links. A natural mix of branded, naked URL, and relevant keyword anchors is ideal. Avoid over-optimization with too many exact-match keyword anchors.
- Brand mentions. Track both linked and unlinked mentions. Unlinked mentions can be opportunities for outreach and link reclamation. They also indicate brand awareness growth.
- Social shares and engagement. While not direct ranking factors, these metrics can indicate content quality and potential for natural link building. They often correlate with increased brand visibility.
- Target page rankings. Monitor ranking changes for pages receiving new links. Improvements can indicate link building success, though consider other factors affecting rankings too.
- Domain Rating or Domain Authority. Track overall site authority metrics. Steady growth can indicate successful, diverse link building. Use tools like Ahrefs or Moz for these metrics.
Content Performance and Efficiency
Key metrics for tracking the efficiency of your content SEO efforts:
- Organic entrances per page. Measures how many users land on each content piece from search. Indicates content visibility and search relevance. Compare across different content types to identify what resonates with your audience and search engines.
- Average time on page and scroll depth. Reflects user engagement and content quality. Longer time and deeper scrolls generally indicate valuable content. However, interpret in context of content purpose – some pages aim for quick information delivery.

- Bounce rate and exit rate. Shows how often users leave after viewing only one page or exit from a specific page. High rates might indicate content mismatch with search intent or poor user experience. Compare against site average and similar content pieces.
- Conversion rate per content piece. Measures how effectively content drives desired actions (e.g., newsletter signups, product purchases). Helps identify high-performing content for business goals. Set up goal tracking in analytics to monitor this accurately.
- Keyword rankings and featured snippets. Track how content ranks for target keywords and ability to capture featured snippets. Indicates search visibility and content optimization effectiveness. Monitor changes over time and after content updates.
3. How to Track: Choose Accurate SEO Tracking Tools
Google Search Console & Google Analytics
Google Search Console (GSC) provides direct insights from Google about your site’s search performance. It shows keyword rankings, click-through rates, indexing status, and technical issues. It offers the most accurate data on how Google views and interacts with your site.
Google Analytics (GA) tracks user behavior on your site. It shows traffic sources, user engagement metrics, and conversion data. It allows you to segment organic traffic and analyze user journeys, helping you understand the impact of SEO on overall site performance.
For more information about using google Analytics for SEO performance, read How to Use Google Analytics 4 for SEO: 7 Ways
Rank Trackers
Rank tracking tools monitor your website’s position in search engine results for specific keywords. They provide more comprehensive ranking data than Search Console, often including competitor rankings and SERP feature tracking. These tools are essential for understanding your visibility in search results and tracking progress over time.
The downside of many rank trackers is that they are not free to use (unlike Google analytics tools) and you need to check data for accuracy and relevancy.
Examples: SE Ranker, AccuRanker
For more information about rank trackers and how to choose one for your needs, read our guide on best while label rank trackers.
Technical SEO Tools
These tools analyze various technical aspects of your website that impact SEO, such as site speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability. They help identify and diagnose technical issues that could be hindering your search performance. Technical SEO tools are crucial for maintaining a healthy, search-engine-friendly website structure.
Examples: Screaming Frog, Sitebulb.
4. How to Report: Choose Intuitive Reporting Tools
Reporting is an integral part of tracking SEO performance, but many tools can overwhelm users with excessive information or prove difficult to customize for specific needs. The key is to select reporting tools that offer clarity and flexibility.
Look for SEO reporting tools that:
- Provide customizable dashboards
- Allow easy data visualization
- Offer integration with multiple data sources
- Enable automated report generation
Prioritize solutions that let you focus on the metrics most relevant to your goals. A good reporting tool should make it easy to spot trends, identify issues, and communicate progress to stakeholders.
5. When to Report: Choose Optimal Reporting Frequency
Reporting and tracking go hand-in-hand: how often you report on SEO will affect how closely you will be tracking SEO results. The optimal reporting frequency depends on your key success metrics and overall SEO strategy.
Here’s a guide to help you determine the right frequency:
If you’re focused on a particular set of keywords, report every 2-4 weeks. Keyword rankings can fluctuate frequently, but meaningful trends usually emerge over this timeframe.
If you’re focused on local SEO, consider monthly reporting. Local SEO metrics like Google Business Profile insights, local pack rankings, and review metrics tend to show meaningful changes over longer periods.
For overall organic traffic and conversions, monthly or quarterly reporting is often sufficient. These metrics typically show more stable trends over time, and longer intervals allow you to account for seasonal variations and see the impact of implemented changes.
For technical SEO issues, set up weekly automated checks but report on a monthly basis. This ensures you catch critical issues quickly while providing a broader view of your site’s technical health over time.
For more insights, feel free to read our detailed guide on SEO reporting.
6. Putting It All Together
SEO Tracking Template #1: All-in-one Search Console Template
Best for:
- General performance data on how often people see your website in search results and click your pages
- Overview of your organic performance in different geographies and on different devices.
- Unique pages and unique keywords insights
SEO Tracking Template #2: Ultimate Keyword Ranking Report
Best for:
- Critical business information about how your content keywords rank over time
- Learning how keyword rankings fluctuate over time
- Learning what keywords drive the most organic traffic to my website
SEO Tracking Template #3: Local SEO Report Template
Best for:
- Deep relevant insights about Local SEO performance
- Analyzing how successful are your local SEO campaigns compared to other marketing channels you utilize
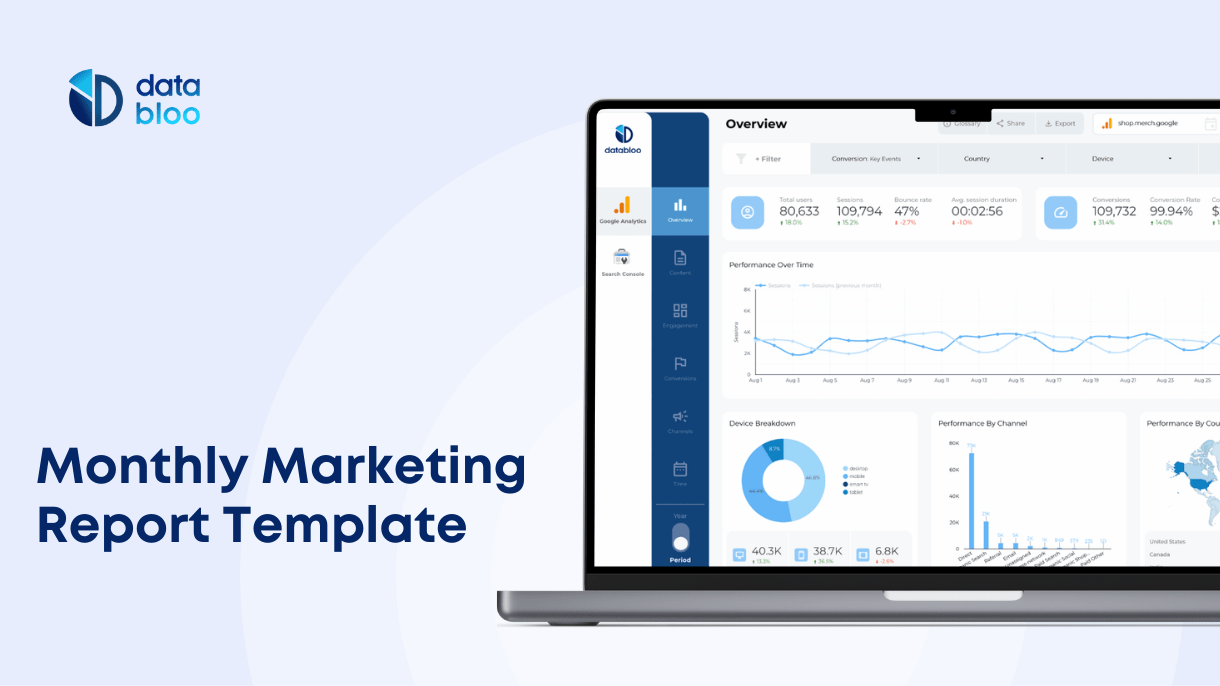
SEO Tracking Template #4: GA4 Ecommerce Revenue Template
Best for:
- Tracking how SEO affects e commerce revenue
- Funnel analysis
- Deep audience insights
(Bonus) Consider Advanced SEO Tracking Techniques
Brand vs Non Brand Keyword Performance
Separate tracking for branded and non-branded keywords provides deeper insights into your SEO strategy’s effectiveness. While branded searches indicate brand strength, non-branded keyword performance shows your content’s ability to attract new audiences and compete in broader markets.
Recommended read: How to Group Branded And Non-Branded Organic Keywords
Cross-Device Tracking
Implement tracking across desktop, mobile, and tablet devices to understand how users interact with your site on different platforms. This helps in optimizing user experience and content for each device type, crucial in today’s mobile-first indexing environment.
Multi-channel Tracking

View SEO as part of a larger digital marketing ecosystem. Integrate SEO tracking with data from other channels like PPC and social media marketing to understand how organic search contributes to overall marketing performance and user journeys.